
09 Jul Leptospirosis
An overview of a major infectious disease of the dog
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease of worldwide significance which affects many species including humans (more commonly known as Weil’s disease). It is maintained in nature by numerous wild and domestic animal reservoir hosts and is zoonotic. It is caused by spiral shaped bacteria called Leptospira interrogans and the serotypes in the four main serogroups of leptospirosis seen across Europe are Icterohaemorrhagiae, Canicola, Australis, Grippotyphosa . These multiply rapidly when entering the blood stream affecting organs such as the liver and kidney.
The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as age, immune response, vaccination status, the strain of Leptospira, and other considerations. Some dogs may have mild symptoms or no symptoms at all, but severe cases can be fatal. While cats can be infected, they rarely show signs of disease. It is much more of a problem in dogs, people and livestock.
Mode of transmission
It is transmitted through the urine of an infected animal which contaminates grass, soil or puddles etc. Rats are generally the primary hosts. Secondary hosts or carriers that have ingested the bacteria include a wide range of other mammals such as dogs, cows, hedgehogs and sheep. Pet to human transmission is through direct or indirect contact with contaminated animal tissue, organs, or urine and the incubation periods range from 5-15 days.
Four main species of Leptospira strains seen in dogs
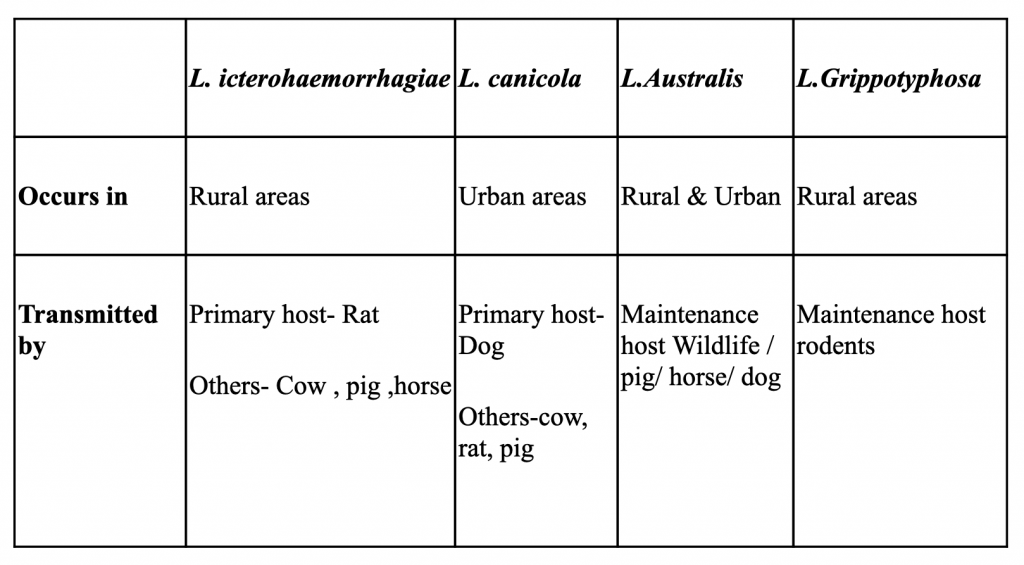
Prognosis and Prevention
Prevention is primarily routine vaccination among others. Two doses are required in any age of dog for primary vaccination, approximately 3-4 weeks apart. Annual vaccinations against the disease are required thereafter due to the property of the vaccines and owners must be conscientious in this respect. Other control measures include inhibiting access of the pet to slow moving water/ponds and implementing strict hygiene measures. It is vital to seek veterinary attention whenever a pet is unwell as it could be a very serious disease process that requires early intervention to try and obtain a satisfactory outcome.



